
What are the tolerances for DIN ISO 2768-2?Īccording to DIN ISO 2768-2. Location Tolerance (Location Deviation) Run-out Tolerance (Run-out Deviation) What is S in GD?ġ.10 The Virtual Condition: Under the impact of the Material Condition (Tolerance Zone Size) modifiers (S) or (M), the Virtual Condition of a feature is a fixed, in-space boundary generated by the collective effects of all the imposed controls.įorm Tolerance (Form Deviation) Form Tolerance and Location Tolerance (Profile Tolerance of Line / Profile Tolerance of Plane) Orientation Tolerance. For a shaft of the same size, h6 would mean 10+0−0.009, which means the shaft may be as small as 0.009 mm smaller than the base dimension and 0 mm larger. H7/h6 is a very common standard tolerance which gives a tight fit. International Tolerance grades For example: H7 (hole, tapped hole, or nut) and h7 (shaft or bolt). Tolerance class designation (description) ISO 2768 Permissible deviations in mm for ranges in nominal lengths What is the standard tolerance for metric? If 2(a) is used to manufacture the part, a hole diameter of 0.502 is acceptable. A tolerance on a radius might be looser than intended, while one on a diameter might be tighter than intended. What is the tolerance for radius?Ī tolerance on a radius will be doubled when measured as a diameter. The tightest machining tolerances possible are in the range of ☐.001”, roughly the width of a human hair. Part 1: General Tolerances ISO 2768-1 is intended to simplify drawing indications and specifies general tolerances in 4 tolerance classes (f – fine, m – medium, c – coarse, v – very coarse).Ī standard tolerance for a CNC machining service is typically ± 0.005”. What are the four tolerance classes in DIN ISO 2768? m class is specified in ISO 2768-1 and K class is specified in ISO 2768-2, which including H, K, and L tolerance levels.
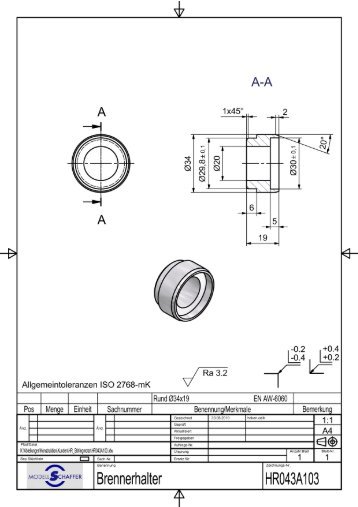
An ISO 2768-mK mark means the dimension information for which the tolerances are not specified will be followed according to the m and K class.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
